Those Eureka Moments..
By James Thompson | 15.10.2013
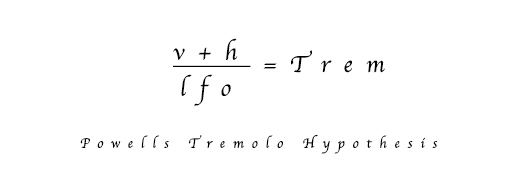
Sampled instrument designers have always struggled with the Vibraphone – the ‘snapshot’ nature of sampling doesn’t really suit it at all; if you sample the single notes, then each notes tremolo will be out of time with the next, and of course the speed will be fixed at one rate anyway. Sometimes people go ahead and sample it anyway, and offer it out of sync with a choice of rates ( fast, medium, slow), but that tends to sound pretty wrong.
The more common ‘workstation’ approach was always to simply switch the motor to off on the Vibraphone, record it static, then fake the tremolo in the synth/sampler using an LFO with a bit of filter and amplitude modulation. Which, in the context of workstation sounds, doesn’t do too bad a job, in that ‘Mock-Tudor’ style that workstation sounds have.
But about a year or 18 months ago, Dan hit on an idea – whether in the bath, I know not – and like many breakthrough ideas, it was beautiful in its simplicity.
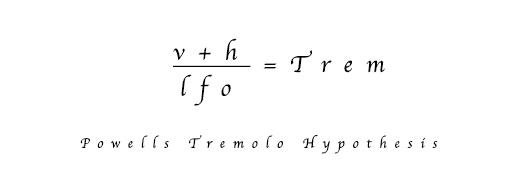
Powell hypothesised that if one recorded the vibraphone twice, in a static state each time, once with the motorised fans fully open, in the vertical position (v) and then again with the fans completely closed, in the horizontal position (h), then by simply crossfading between the two with a simple sine LFO in the sampler, you would get a very natural tremolo effect (Tr).
The only way to test the hypothesis, however, was to actually record the vibraphone – twice – with no real idea if it would actually work ( ie : ‘sound good’) when finished. Bravely we pressed ahead. Enlisting the help of lab assistant Ed, an instrument was sourced (a Yamaha YV-3910M ‘Professional Gold’), and a studio booked for January 2013. For this project we returned to Peter Gabriel’s Real World Studio – a favourite of ours, but one from which we had been away for more than ten years.

The vibraphone session at Real World. Not as much fun as you might think.
It was a long session- two full 12 hour days listening intently to the metallic ring of the vibraphone key takes its toll on the strongest of men. This was not just one vibraphone sampling session, after all – after we had recorded the entire instrument, every key, with 20+ velocities several times each for round robins, damped and undamped – we then did it all over again again, with the fans closed.
Even once the recording was complete, we were still not able to test Powell’s Hypothesis. First, the samples had to be edited – 3,864 of them, as it turned out. Finally, after months of painstaking work, in the summer of 2013, our small but dedicated team prepared to put the theory into practice.
Did it work? You can judge. Check out our Vibraphone Now!